- +91 62384 78716 +91 99475 78797
-
Sasthamangalam, Trivandrum
Sasthamangalam, Trivandrum
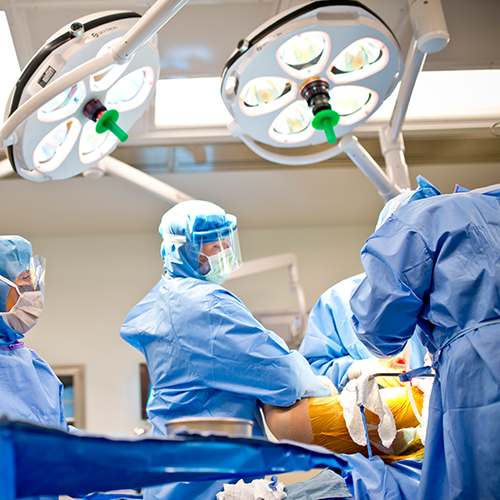
Hip replacement surgery is considered amongst the most successful operations in all of medicine. Since the early 1960s, improvements in surgical techniques and technology have tremendously increased the effectiveness of total hip replacement. Patients are able to go from being bedridden to walking freely without support within few days of surgery.
The most typical cause of long duration hip pain and functional disability is arthritis.
Osteoarthritis – age-related “wear and tear” kind of arthritis which normally occurs in people aged 50 years and above.
Rheumatoid arthritis – an autoimmune disease in which the synovial membrane becomes thickened and inflamed leading to damage of the cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness
Post-traumatic arthritis – following a serious hip injury or fracture where the cartilage may become damaged
Osteonecrosis – due to limitation in the blood supply to the femoral head causing the surface of the bone to collapse and resulting in arthritis
Childhood hip disease – infants and children with hip problems may cause arthritis later on in life as the hip may not grow normally
In hip replacement surgery, the damaged cartilage and bone is shaved and replaced by prosthetic parts.
The surgical procedure usually takes from 1 to 2 hours..
After surgery, you will be taken care of by specialised nursing team in the recovery room for several hours while your recovery is monitored. You will then spend next 3-4 days in the room where your further recovery is monitored by your doctor and physiotherapy team.
The success of your surgery will depend largely on how well you follow your physiotherapist’s and orthopaedic surgeon’s instructions regarding home care during the first few weeks after surgery.
Copyright © 2025 Dr. Ganesh Navaneedhan. All Rights Reserved. | Designed By Harvee healthcare